JobSystemまなび
概要
学ぶ。
面倒臭い人は最後だけ見ると良い。
途中経過
こんな感じのコードにしてみる
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Unity.Collections;
using UnityEngine;
public class JS : MonoBehaviour
{
[SerializeField] Transform[] targets;
float[] velocity;
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
velocity = new float[targets.Length];
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
var commands = new NativeArray<RaycastCommand>(targets.Length, Allocator.TempJob);
var results = new NativeArray<RaycastHit>(targets.Length, Allocator.TempJob);
for (var i = 0; i < targets.Length; i++)
{
var targetPosition = targets[i].position;
var direction = Vector3.down;
// 指定位置から下方向にレイキャストを行うコマンドをまとめる
// RaycastCommand型は、結果にReycastHit型を返してくる。
var command = new RaycastCommand(targetPosition, direction);
commands[i] = command;
}
/*
コマンドを実行、結果はresultsに入る。
RaycastCommandで入力したコマンドは、RaycastHitを返してくる。
(これはraycastCommand型のScheduleBatch関数がそういう実装になってる)
*/
// 完了まで待つ(ここでデッドロックしないのはなぜなんだろう、継続になってる? それともそういうのを加味しないでいいくらい高速?)
// -> 待ってる。十分に高速なら問題ないというロジック。
// 最後の引数はjobの最大分散数。
var commandJobHandle = RaycastCommand.ScheduleBatch(commands, results, 10);
// jobHandleの終了を待つ
commandJobHandle.Complete();
// 破棄
commands.Dispose();
// 加速度をセット、速度がマイナス(下に移動)、かつレイキャストの距離が一定以下だったらぶつかったとみなす。
for (var i = 0; i < targets.Length; i++)
{
if (velocity[i] > 0 && results[i].distance < 0.5f)
{
velocity[i] = -2;
}
velocity[i] += 0.098f;
}
results.Dispose();
// 加速度分移動
for (var i = 0; i < targets.Length; i++)
{
targets[i].localPosition += Vector3.down * velocity[i];
}
}
}
前提として、targets配列にはエディタ上でcubeオブジェクトをセットしておく。
あと、ヒット対象となる地面(Terrainとか)を用意しとく。
結果
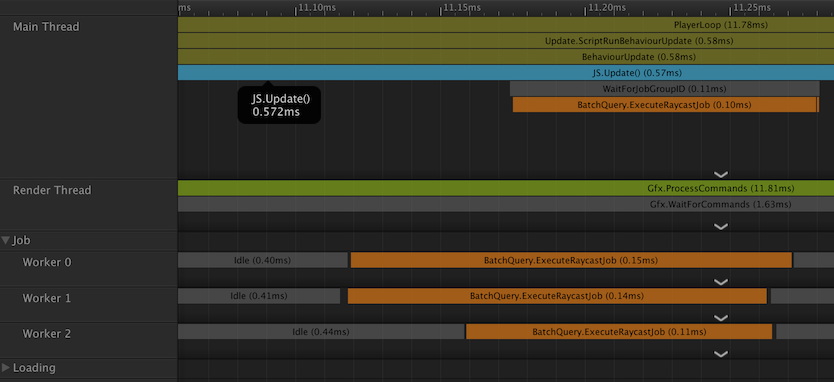
いい感じにMainと他3スレッド(マシンが4コアなので合計4)で分散できた。
これワーカー数はコア数と一致するんだろうか、、

アップで見るとこんな感じで、
・どれか一つのスレッドがResultJobを実行
・メインスレッドのWaitForJobGroupIDがそれを受ける
みたいな感じに見える。
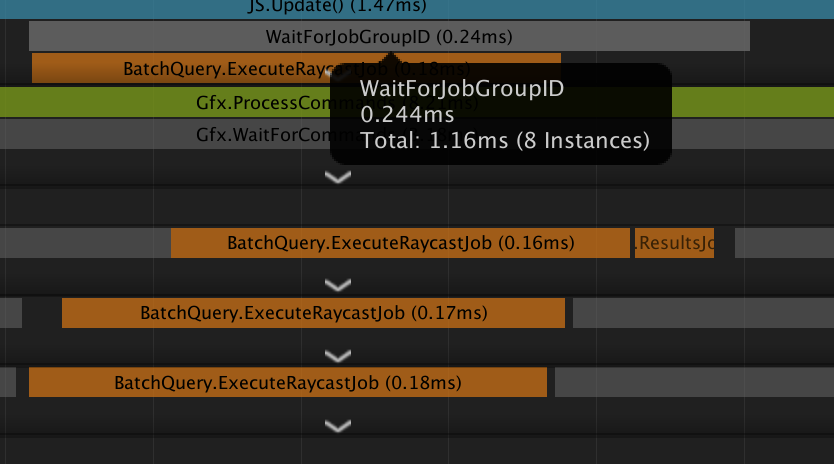
ここまでで、Raycastを打つ部分はJob化できてる。で、次に
・ヒットチェックして加速度を 制御する部分
・移動させる部分
をJob化してみる。
この時点で100fps前後。
ヒットチェック部分のJob化
グローバルに定義してあるvelocityはNativeArray<float>にしておく。
このあとJobからアクセスする要素を生成する時に代入するため。
NativeArray<float> velocity;
んで、このインスタンスはOnEnableで生成、OnDisableで削除するようにする。
void OnEnable()
{
velocity = new NativeArray<float>(targets.Length, Allocator.Persistent);
for (int i = 0; i < targets.Length; i++)
{
velocity[i] = 1;
}
}
void OnDisable()
{
velocity.Dispose();
}
そんでまずHitCheckJobを、IJobParallelFor structを拡張する形で定義。
struct HitCheckJob : IJobParallelFor
{
[ReadOnly] public NativeArray<RaycastHit> hits;
public NativeArray<float> velocities;
public void Execute(int i)
{
// 加速度をセット、速度がマイナス(下に移動)、かつレイキャストの距離が一定以下だったらぶつかったとみなす。
if (velocities[i] > 0 && hits[i].distance < 0.5f)
{
// ヒットしたので加速度を-2にセットして浮かび上がらせる。
velocities[i] = -2;
}
velocities[i] += 0.098f;
}
}
Jobを定義する際にパラメータに要素をセットすることで、後ほど実行 = Schedule関数を呼ぶ時に第一引数にセットした数だけExecuteが回ってくれる。
hitsなどの要素のセットについては、このジョブのインスタンスを生成する時にhits = みたいな形にして渡す。
hitsは参照オンリーなので、ReadOnlyをつけることができる。(velocityはR/W両方あるのでなんもできん)
次に、レイキャストコマンドを実行する部分の次に、HitCheckJobを生成する部分を追加する。
void Update()
{
var commands = new NativeArray<RaycastCommand>(targets.Length, Allocator.TempJob);
var results = new NativeArray<RaycastHit>(targets.Length, Allocator.TempJob);
for (var i = 0; i < targets.Length; i++)
{
var targetPosition = targets[i].position;
var direction = Vector3.down;
// 指定位置から下方向にレイキャストを行うコマンドをまとめる
// RaycastCommand型は、結果にReycastHit型を返してくる。
var command = new RaycastCommand(targetPosition, direction);
commands[i] = command;
}
// ジョブの初期化をする
var hitCheckJob = new HitCheckJob()
{
hits = results,
velocities = velocity
};
ここまでで、次の状態のhitCheckJobのインスタンスが手に入る。
・このあとRaycastの結果 = RaycastHitのNativeArrayを返してくるresultsの参照を、hitsに代入
・速度が入るvelocityのNativeArrayの参照を、Job内部で値を入れるvelocitiesに代入
そんでjobを実行。
var commandJobHandle = RaycastCommand.ScheduleBatch(commands, results, 10);
var hitcheckHandle = hitCheckJob.Schedule(targets.Length, 10, commandJobHandle);
hitcheckHandle.Complete();
先ほどまでRaycastCommandの結果をそのままCompleteしていたのを、
新たにhitcheckHandleインスタンスをhitCheckJob.Scheduleから生成し、そのjobの完了を待つように変更する。
この際、まずレイキャストを打ってからヒットチェックがしたいため、hitcheckJobのSchedule関数にcommandJobHandleのインスタンスをセット、
必ず
・commandJobHandle
・hitcheckHandle
という順番で処理が実行されるようにする。
ここまでで、ヒットチェックがjob化できた。
移動もJob化する
あとは応用で、
・加速度分移動する
という処理をJob化する。
まず位置(transform)をいじるので、transformに対してJob内から干渉できるJobを作成する。
struct ApplyPositionJob : IJobParallelForTransform
{
[ReadOnly] public NativeArray<float> velocities;
public void Execute(int i, TransformAccess transform)
{
transform.localPosition += Vector3.down * velocities[i];
}
}
こんな感じで、IJobParallelForTransform structを拡張したジョブを定義する。
Executeの内部処理についてはちょっと特殊で、
・IJobOarallelForTransform関数のSchedule関数はTransformAccessArray(Transform[] transforms)という型を引数にとり
・Execute実行時に transforms へのアクセスが可能なように引数に入っている
という感じ。
Transformそのままだと参照型になってしまっていて値型ではないのでJobからアクセスできない、というのがあるらしい。
なので、
var transformAccess = new TransformAccessArray(targets);
とか定義して、Schedule関数に対して渡す。
さらにScheduleの第二引数としてヒットチェックのjobHandleを渡し、順番を制御する。
var applyPosHandle = applyPositionJob.Schedule(transformAccess, hitcheckHandle);
これで、
・レイキャスト
・ヒットチェック
・移動
の順番で処理が行われるようになっている。
処理が終わったら
transformAccess.Dispose();
も忘れないようにする。ない場合エラー出してくれるんで便利。
ここまででヒットチェックと移動のJob化ができた。やったぜ。
この時点で100fps前後。まあ変わらん。
Raycast、Hitcheck、ApplyPosがJob化できた図。
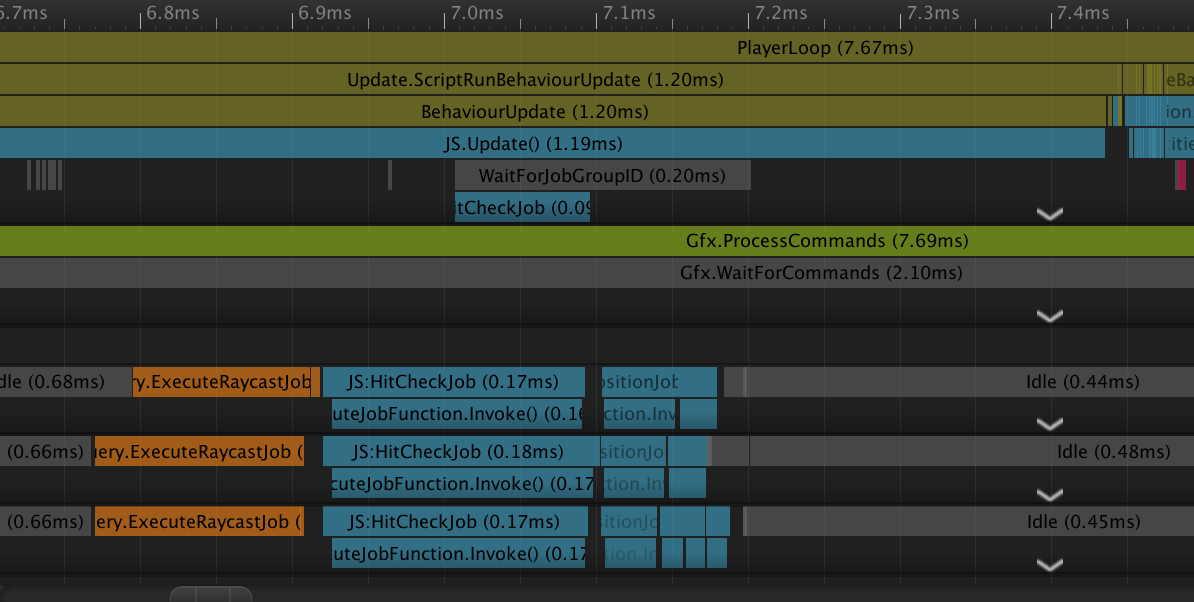
ここからさらに高速化するには、「Completeをやめてメインスレッドのロックを外す」ということをする感じになる。
Completeを次のフレームで実行する(WaitForJobGroupにかかる時間 = メインスレッドでの待ちを減らす)
Updateで行うコードを次のような感じにする。
void Update()
{
// applyPosHandle の終了を待つ
applyPosHandle.Complete();
for (var i = 0; i < targets.Length; i++)
{
var targetPosition = targets[i].position;
var direction = Vector3.down;
// 指定位置から下方向にレイキャストを行うコマンドをまとめる
// RaycastCommand型は、結果にReycastHit型を返してくる。
var command = new RaycastCommand(targetPosition, direction);
commands[i] = command;
}
// ジョブの初期化をする
var hitCheckJob = new HitCheckJob()
{
hits = results,
velocities = velocity
};
var applyPositionJob = new ApplyPositionJob()
{
velocities = velocity
};
// レイキャスト、ヒットチェックまでは変わらず、applyPosのハンドルをグローバル変数に入れる。
var commandJobHandle = RaycastCommand.ScheduleBatch(commands, results, 10);
var hitcheckHandle = hitCheckJob.Schedule(targets.Length, 10, commandJobHandle);
applyPosHandle = applyPositionJob.Schedule(transformAccess, hitcheckHandle);
}
applyPosHandleをグローバルに定義して、その終了待ち=CompleteをUpdateの先頭で行う。
グローバル化に祭して、いままでUpdateの最後でDisposeしていたテンポラリなNativeArrayもすべてグローバルな定義に変わる必要がある。
Jobのインスタンス生成(参照渡し)と、レイキャストコマンドの生成/セットは変わらず。
この時点で103fpsくらいになった。ちょっと高速化。
プロファイラを見てみると、Update関数が実行されてからJobが実行されている。やったぜ。
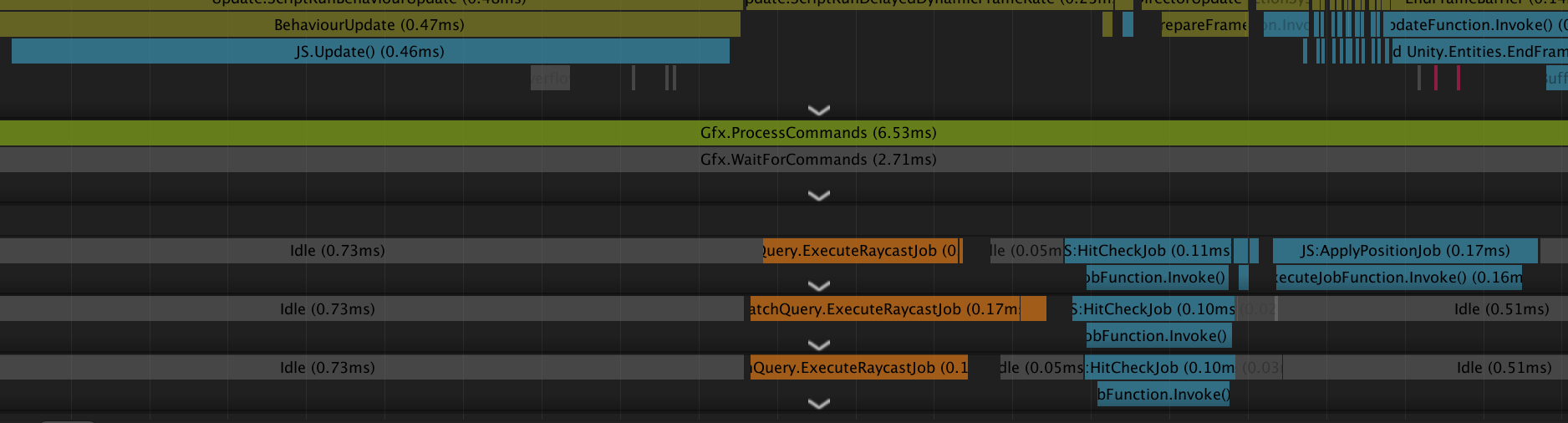
あと、WaitForJobIDが消えた。(乗らないくらい短いか、見落としてるか。)
ちょっとBurst化してみる
JobをBurstCompiler任せにしてみる。
Job定義のstructに BurstCompile のアノテーションをつけるだけ。
-> 爆速になった。
110fpsくらい出てる。
値を得られるようにする
IJobを拡張したstructを用意する。
struct IsHit : IJob
{
[ReadOnly] public NativeArray<RaycastHit> hits;
[WriteOnly] public NativeArray<int> isHit;
public void Execute()
{
for (var i = 0; i < hits.Length; i++)
{
// 距離が1fより小さかったら、ヒットしている
if (hits[i].distance < 1f)
{
isHit[0] = 0;
return;
}
}
// それ以外であればすべてのインスタンスがヒットしてない
isHit[0] = 1;
}
}
Update内でヒットのハンドルを生成、ここでサイズ1のNativeArray<int>を入れる。
var hitHandle = new IsHit()
{
hits = results,
isHit = new NativeArray<int>(1, Allocator.TempJob)
};
// レイキャスト、ヒットチェックまでは変わらず、applyPosのハンドルをグローバル変数に入れる。
var commandJobHandle = RaycastCommand.ScheduleBatch(commands, results, 10);
var isHitHandle = hitHandle.Schedule(commandJobHandle);
var hitcheckHandle = hitCheckJob.Schedule(targets.Length, 10, commandJobHandle);
applyPosHandle = applyPositionJob.Schedule(transformAccess, hitcheckHandle);
// ヒット判定だけは即座に終了させる
isHitHandle.Complete();
var isHit = hitHandle.isHit[0];
if (isHit != 1)
{
Debug.Log("ヒットした");
}
// hitHandleのisHitはこのブロック内で生成しているパラメータなので、ここで消費する。
hitHandle.isHit.Dispose();
isHitHandleを生成、レイキャストのあとに実行する。
で、ヒット判定だけをCompleteにして値を受け取李判断に使う。便利。
コルーチン化する
ちょっとは書きやすくなるか?
IEnumerator Start()
{
var applyPosHandle = default(JobHandle);
var commands = new NativeArray<RaycastCommand>(targets.Length, Allocator.Persistent);
var results = new NativeArray<RaycastHit>(targets.Length, Allocator.Persistent);
var transformAccess = new TransformAccessArray(targets);
var velocity = new NativeArray<float>(targets.Length, Allocator.Persistent);
for (int i = 0; i < targets.Length; i++)
{
velocity[i] = 1;
}
disposeAct = () =>
{
try
{
applyPosHandle.Complete();
velocity.Dispose();
commands.Dispose();
results.Dispose();
transformAccess.Dispose();
}
catch { }
};
// ジョブの初期化をする
var hitCheckJob = new HitCheckJob()
{
hits = results,
velocities = velocity
};
var applyPositionJob = new ApplyPositionJob()
{
velocities = velocity
};
while (true)
{
for (var i = 0; i < targets.Length; i++)
{
var targetPosition = targets[i].position;
var direction = Vector3.down;
// 指定位置から下方向にレイキャストを行うコマンドをまとめる
// RaycastCommand型は、結果にReycastHit型を返してくる。
var command = new RaycastCommand(targetPosition, direction);
commands[i] = command;
}
var hitHandle = new IsHit()
{
hits = results,
isHit = new NativeArray<int>(1, Allocator.TempJob)
};
// レイキャスト、ヒットチェックまでは変わらず、applyPosのハンドルをグローバル変数に入れる。
var commandJobHandle = RaycastCommand.ScheduleBatch(commands, results, 10);
var isHitHandle = hitHandle.Schedule(commandJobHandle);
var hitcheckHandle = hitCheckJob.Schedule(targets.Length, 10, commandJobHandle);
applyPosHandle = applyPositionJob.Schedule(transformAccess, hitcheckHandle);
// ヒット判定だけは即座に終了させる
isHitHandle.Complete();
var isHit = hitHandle.isHit[0];
if (isHit != 1)
{
Debug.Log("ヒットした");
}
// hitHandleのisHitはこのブロック内で生成しているパラメータなので、ここで消費する。
hitHandle.isHit.Dispose();
yield return null;
// applyPosHandle の終了を待つ
applyPosHandle.Complete();
}
}
NativeArrayとか、jobHandleの生成を一度きりにできた。
参照だけをなんとかできるのが良い。
まとめ
コード全体を書いとく。
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Unity.Burst;
using Unity.Collections;
using Unity.Jobs;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.Jobs;
public class JS : MonoBehaviour
{
[SerializeField] Transform[] targets;
[BurstCompile]
struct HitCheckJob : IJobParallelFor
{
[ReadOnly] public NativeArray<RaycastHit> hits;
public NativeArray<float> velocities;
public void Execute(int i)
{
// 加速度をセット、速度がマイナス(下に移動)、かつレイキャストの距離が一定以下だったらぶつかったとみなす。
if (velocities[i] > 0 && hits[i].distance < 0.5f)
{
// ヒットしたので加速度を-2にセットして浮かび上がらせる。
velocities[i] = -2;
}
velocities[i] += 0.098f;
}
}
[BurstCompile]
struct ApplyPositionJob : IJobParallelForTransform
{
[ReadOnly] public NativeArray<float> velocities;
public void Execute(int i, TransformAccess transform)
{
transform.localPosition += Vector3.down * velocities[i];
}
}
[BurstCompile]
struct IsHit : IJob
{
[ReadOnly] public NativeArray<RaycastHit> hits;
[WriteOnly] public NativeArray<int> isHit;
public void Execute()
{
for (var i = 0; i < hits.Length; i++)
{
// 距離が1fより小さかったら、ヒットしている
if (hits[i].distance < 1f)
{
isHit[0] = 0;
return;
}
}
// それ以外であればすべてのインスタンスがヒットしてない
isHit[0] = 1;
}
}
private Action disposeAct = () => { };
IEnumerator Start()
{
var applyPosHandle = default(JobHandle);
var commands = new NativeArray<RaycastCommand>(targets.Length, Allocator.Persistent);
var results = new NativeArray<RaycastHit>(targets.Length, Allocator.Persistent);
var transformAccess = new TransformAccessArray(targets);
var velocity = new NativeArray<float>(targets.Length, Allocator.Persistent);
for (int i = 0; i < targets.Length; i++)
{
velocity[i] = 1;
}
disposeAct = () =>
{
try
{
applyPosHandle.Complete();
velocity.Dispose();
commands.Dispose();
results.Dispose();
transformAccess.Dispose();
}
catch { }
};
// ジョブの初期化をする
var hitCheckJob = new HitCheckJob()
{
hits = results,
velocities = velocity
};
var applyPositionJob = new ApplyPositionJob()
{
velocities = velocity
};
while (true)
{
for (var i = 0; i < targets.Length; i++)
{
var targetPosition = targets[i].position;
var direction = Vector3.down;
// 指定位置から下方向にレイキャストを行うコマンドをまとめる
// RaycastCommand型は、結果にReycastHit型を返してくる。
var command = new RaycastCommand(targetPosition, direction);
commands[i] = command;
}
var hitHandle = new IsHit()
{
hits = results,
isHit = new NativeArray<int>(1, Allocator.TempJob)
};
// レイキャスト、ヒットチェックまでは変わらず、applyPosのハンドルをグローバル変数に入れる。
var commandJobHandle = RaycastCommand.ScheduleBatch(commands, results, 10);
var isHitHandle = hitHandle.Schedule(commandJobHandle);
var hitcheckHandle = hitCheckJob.Schedule(targets.Length, 10, commandJobHandle);
applyPosHandle = applyPositionJob.Schedule(transformAccess, hitcheckHandle);
// ヒット判定だけは即座に終了させる
isHitHandle.Complete();
var isHit = hitHandle.isHit[0];
if (isHit != 1)
{
Debug.Log("ヒットした");
}
// hitHandleのisHitはこのブロック内で生成しているパラメータなので、ここで消費する。
hitHandle.isHit.Dispose();
yield return null;
// applyPosHandle の終了を待つ
applyPosHandle.Complete();
}
}
void OnDisable()
{
disposeAct();
}
}
JobSystemは、次のようなもの
・IJob系を継承したstructを定義すると、Executeメソッド内がworkerスレッド内で実行される。
IJob Execute()
IJobParallelFor Execute(index)
IJobParallelForTransform Execute(index, transformAccess)
など、namespace Unity.Jobs 以下のもの。
これにより、Execute内に書いた処理がworkerスレッドで分散して高速に実行される。
Executeメソッド内では、structに定義したパラメータに触れるほか、indexを使ってパラメータの特定のindexに対して変更をかけたりができる。
イメージ的には、Executeメソッドは一つのworkerスレッドからアクセスされるものではなく、
複数のworkerスレッドから実行されえる。そのため、indexパラメータが渡ってくるがその実行元がどのworkerかはわからない。
・IJob系のstructをインスタンス化し、Schedule関数を実行すると、Jobがスケジューリングされてworkerスレッドで実行される。
インスタンス化時に、各ジョブを跨いで編集する対象をセットする。
JobAインスタンス{ param1 = shared1 }
JobBインスタンス{ param2 = shared1 }
のように、shared1というパラメータを各ジョブで共有させることで、一つのパラメータを複数のジョブでガチャガチャ編集することができる。
・Jobのスケジューリング時に、引数として
IJob Schedule(完了を待つほかのJob)
IJobParallelFor Scuedule(扱う対象の数, 分散するworker数みたいな数値, 完了を待つほかのJob)
IJobParallelForTransform Scuedule(TransformAccessArray, 完了を待つほかのJob)
などを渡せる。
・Jobの実行待ちは、Complete関数で行うことができる。
・NativeArray<T>を使って、Job(Workerスレッド)からアクセスする要素を定義する。
・NativeArray<T>はかならずDisposeする必要がある。